Textile Pests Although it’s actually the larvae of these pests which causes visible damage to our homes and businesses rather than the fact that they’re trying to eat our prized possessions, they can still cause significant damage to many areas of the home. Items most at risk include clothing, upholstered furniture, woollen carpets and collections of valuable textile items. If left untreated, textile pests can cause irreplaceable damage so it’s important to identify the signs of an infestation as quickly as possible. Some of the signs we have listed below.
 Damage in a targeted area
Damage in a targeted area
 live or dead adult insects gathered around window openings
live or dead adult insects gathered around window openings
 Damage to natural fabrics
Damage to natural fabrics
 Brushes or paintbrushes made with natural bristles
Brushes or paintbrushes made with natural bristles
 Damage to Tapestries, carpets, rugs, book bindings,
Damage to Tapestries, carpets, rugs, book bindings,
furniture, matresses, pillows, cushions, silk and feathered items.

TEXTILE PESTS
Varied Carpet Beetle ( Anthrenus Verbasci )
Carpet beetle larvae, known as ‘woolly bear’, are banded in appearance and covered in short bristles – up to 5mm. They look like small, furry caterpillars. Once wooly bears turn into grown beetles, they are a round shape with six legs and antennae. They tend to roll up when disturbed. As they grow, they moult – and the old cast-off skins may be the first sign of infestation. Adults are often seen in April, May and June, seeking egg-laying sites; and the grubs are most active in October before they hibernate.
The adult Carpet Beetle feeds only on pollen and nectar of garden flowers but lays its eggs in old birds’ nests, felt, fabric or accumulated fluff in buildings. It is the larvae from these eggs that do the damage. They feed on feathers, fur, hair, or wool and tend to wander along the pipes from roofs into airing cupboards – which house the clothes and blankets which constitute the food.
How do you prevent carpet beetles?
- Clean regularly and thoroughly
- Keep food in well-sealed containers
- Install bug nets over windows and doors
- Inspect plants and flowers before bringing them indoors
- Seal any cracks and gaps around doors and windows
How to get rid of carpet beetles
To get rid of carpet beetles you can clean infested areas using a nozzle vacuum cleaner, concentrating on removing debris and larvae from cracks and crevices. An application of a residual insecticide should then be made to the area, concentrating on treating cracks and crevices. Dust formulations, including desiccant dusts, will be effective but may be vacuumed away in subsequent cleaning.
To get rid of carpet beetles permanently, it is always most effective to call in a licensed pest control expert like Environmental Pest Solutions for a professional carpet and textiles treatment.
Give us a call to sort any textile pest infestations,
use our contacts page.

Fur Beetle ( Attagenus Pelio )
An oval black beetle 4-6mm long with a white spot on each wing case. They are coloured black, but for small patch of white hairs on either side of elytra, base of thorax also covered with white hairs; larvae have distinctive tuft of very long hairs which project backwards. They can often be detected by their cast-off skins as they moult. Grubs feed on fur, hair, skins, feathers and wool and may damage the upholstery.
Control Methods
A mixture of white or apple cider vinegar and water can be applied to shelves, drawers, hangers, window sills and cupboards to remove any dirt or food residue. Applying boric acid. Sprinkling this mild insecticide on carpets, rugs and furniture will kill any remaining beetles. Environmental Pest Solutions have professional methods and treatments to eradicate any textile pest.
Give us a call to sort any textile pest infestations,
use our contacts page.
Leather Beetle ( Dermestes Maculatus )
Forewings hard and leathery, meeting along mid-line of dorsal surface; hind- wings membranous, sometimes lacking; biting mouthparts; well- developed thorax; complete metamorphosis with egg, larval, pupal and adult stages. Densely covered with hairs or scales; 5–11 segmented antennae with distinct club; 5-segmented tarsi.
- Adults, 5.5 -10 mm long; body, oval-shaped and densely covered with round scale-like hairs
- Thorax with patches of white hairs on the sides
- Elytra: uniformly coloured brown/black with an even scattering of white hairs
- Underside predominantly white
- Inner apex of each elytron produced backwards into a fine point
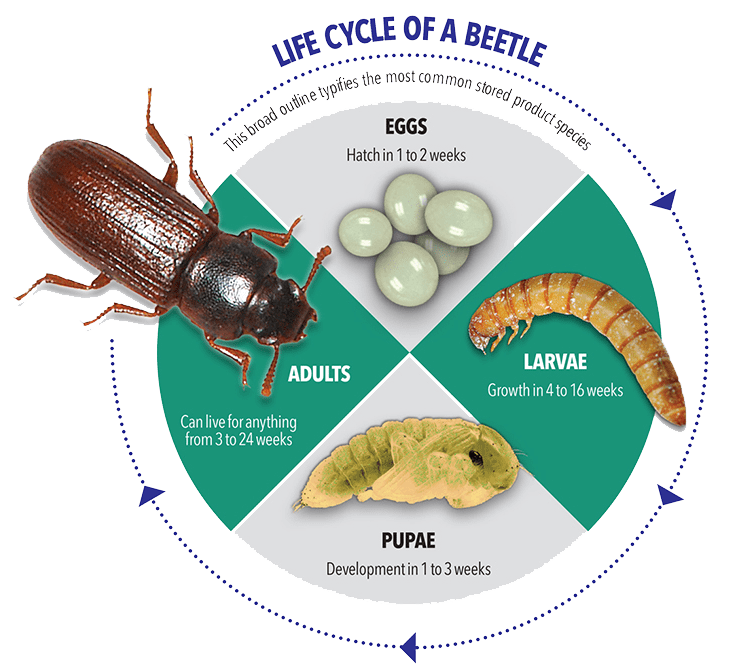
Life Cycle
Two to Three months, given the right conditions.
Control Methods
Control of these pests begins with a thorough inspection, source the location and then the destruction of the source. Within commercial situations, the use of insect monitors is key to help pinpoint the infestations. A thorough clean up is advised, using a vacuum cleaner to get into the cracks and crevices followed by a treatment using a broad spectrum residual insecticide.
Whether in a commercial or domestic setting, Environmental Pest Solutions can assist you in completely ridding your property of any Textile Pest. Our expert team will work quickly and efficiently to remove the problem with minimal disruption.
